Female Temple Hair Loss: Causes, Prevention Tips, and Treatment Options
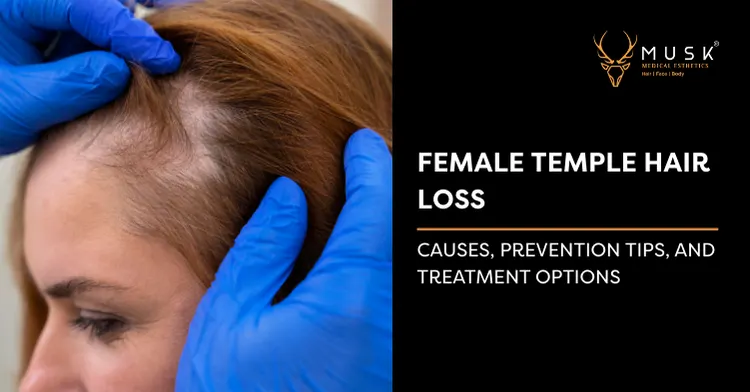
Losing hair can be a distressing experience, especially when it affects noticeable areas like your temples. While often associated with men, female temple hair loss is more common than you might think and can significantly impact self-esteem. At Musk Clinic, we understand your concerns and are here to provide clear, actionable insights into this often-misunderstood condition.
What is temple hair loss in women?
Temple hair loss refers to the thinning or receding of hair in the areas on either side of your forehead, above your ears. It can manifest as a widening part, a general decrease in hair density, or a noticeable recession of the hairline in these specific regions.
Why is this happening to my temples?
The causes of female temple hair loss are multifaceted, ranging from hormonal fluctuations to lifestyle factors. Identifying the root cause is the first step toward effective management and treatment. Let's discuss some of the most common culprits.
Hormonal Imbalances:
- Androgenetic Alopecia (Female Pattern Hair Loss):
This is the most common cause of hair loss in women. It's hereditary and influenced by androgens (male hormones present in women). It often presents as a widening part and diffuse thinning, which can include the temples.
- Postpartum Hair Loss (Telogen Effluvium):
Pregnancy brings a surge in hormones that keep hair in its growth phase. After childbirth, these hormone levels drop, leading to a sudden shedding of hair, including from the temples, typically three to six months later.
- Menopause and Perimenopause:
As women approach and go through menopause, estrogen levels decrease, which can lead to hair thinning and loss. This hormonal shift often impacts hair density across the scalp, including the temple areas.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both an overactive (hyperthyroidism) and underactive (hypothyroidism) thyroid can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to generalized hair thinning that may include the temples.
Nutritional Deficiencies:
- Iron Deficiency (Anemia):
Iron is crucial for hair growth. A lack of sufficient iron can lead to hair follicles not receiving enough oxygen, resulting in hair loss.
- Vitamin D Deficiency:
Vitamin D plays a vital role in hair follicle cycling. Insufficient levels can lead to poor hair growth and increased shedding.
- Biotin and Zinc Deficiencies:
While less common, deficiencies in these essential nutrients can also contribute to hair thinning and loss.
Stress and Lifestyle Factors:
- Chronic Stress (Telogen Effluvium):
Prolonged emotional or physical stress can push a large number of hair follicles into a resting phase prematurely, leading to significant shedding a few months later.
- Harsh Hairstyles:
Tight ponytails, braids, and buns can cause traction alopecia, a form of hair loss due to constant pulling on the hair follicles. The temples are particularly vulnerable to this.
- Heat Styling and Chemical Treatments:
Frequent use of hot styling tools and chemical processes like perms or relaxers can damage hair shafts and follicles over time, leading to breakage and thinning.
Medical Conditions and Medications:
- Autoimmune Diseases:
Conditions like alopecia areata, lupus, or psoriasis can cause hair loss in patches, which may include the temple area.
- Medications:
Certain medications, such as those for blood pressure, depression, or chemotherapy, can have hair loss as a side effect.
- Scalp Infections:
Fungal or bacterial infections of the scalp can lead to inflammation and hair loss in affected areas.
How can I prevent temple hair loss? Prevention is often better than cure!
While some causes of hair loss are beyond our control, many preventive measures can significantly reduce your risk and maintain healthy hair.
Prevention Strategies for Female Temple Hair Loss
| Category | Prevention Tip | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Hair Care | Gentle Styling Habits | Avoid tight hairstyles (ponytails, braids, buns) that pull on the hair. Opt for looser styles. Reduce heat styling (flat irons, curling irons) and allow hair to air dry when possible. Use heat protectants. |
| Choose Hair-Friendly Products | Use sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners. Avoid products with harsh chemicals. Look for fortifying ingredients like biotin, keratin, and natural oils. | |
| Diet & Nutrition | Balanced Diet | Ensure a diet rich in proteins (lean meats, fish, beans), iron (spinach, lentils), zinc (nuts, seeds), biotin (eggs, avocados), and vitamins (fruits, vegetables). |
| Hydration | Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your body and hair follicles hydrated. | |
| Lifestyle | Stress Management | Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature. Ensure adequate sleep (7-9 hours per night). |
| Regular Exercise | Improves blood circulation, which helps deliver nutrients to the scalp and hair follicles. | |
| Medical Check-ups | Address Underlying Health Issues | Regularly consult your doctor for blood tests to check for thyroid issues, iron deficiency, and other hormonal imbalances. Treat any underlying medical conditions promptly. |
| Sun Protection | Protect Scalp from Sun | Wear hats or use UV protection sprays on your scalp, especially if your hair is thinning. Sun damage can weaken hair follicles. |
| Avoid Smoking | Quit Smoking | Smoking reduces blood flow to the scalp and can negatively impact hair health, hindering growth and contributing to thinning. |
What are my treatment options for female temple hair loss?
If you're already experiencing temple hair loss, don't despair! At Musk Clinic, we offer a range of advanced and personalized treatment options designed to stimulate regrowth and improve hair density.
Over the Counter and Topical Treatments:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine):
This is the only FDA-approved topical treatment for female pattern hair loss. It works by increasing blood flow to the hair follicles, extending the growth phase, and encouraging thicker hair growth. It's available in different strengths and applied directly to the scalp.
- Ketoconazole Shampoos:
While primarily used for dandruff, some studies suggest that ketoconazole can have anti-androgenic effects, potentially benefiting hair loss related to hormonal factors.
- Caffeine-infused Shampoos and Serums:
Caffeine is believed to stimulate hair growth by blocking the effects of DHT (a hormone linked to hair loss) and improving blood circulation to the scalp.
Prescription Medications:
- Spironolactone: :
This oral medication is an anti-androgen that can be prescribed for women with hormonal hair loss, especially if their androgen levels are elevated. It helps block the effects of androgens on hair follicles.
- Finasteride (Off-label for Women):
While primarily used for dandruff, some studies suggest that ketoconazole can have anti-androgenic effects, potentially benefiting hair loss related to hormonal factors.
- Oral Minoxidil (Low-Dose):
Increasingly, low-dose oral minoxidil is being prescribed for diffuse hair loss, including temple thinning, with promising results and generally good tolerability.
Advanced Therapies at Musk Clinic:
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
PRP involves drawing a small amount of your blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets (rich in growth factors), and then injecting this plasma into your scalp. These growth factors stimulate dormant hair follicles and promote new hair growth.
- Mesotherapy:
This technique involves injecting a cocktail of vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and other nutrients directly into the mesoderm layer of the scalp. It aims to nourish hair follicles, improve circulation, and stimulate hair growth.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT):
LLLT uses medical-grade lasers to deliver photons to the scalp. These light particles are absorbed by the hair follicles, stimulating cellular activity, extending the growth phase, and encouraging thicker hair.
Surgical Options:
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE):
This is a minimally invasive procedure where individual hair follicles are extracted from a donor area (usually the back of the scalp) and meticulously transplanted to the thinning temple regions. FUE leaves no linear scar and offers a natural-looking result.
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT):
In this procedure, also known as the 'strip method,' a thin strip of hair-bearing skin is removed from the donor area. Follicles are then extracted from this strip and transplanted to the temple regions. FUT is highly effective for transplanting a large number of grafts in a single session.
- Direct Hair Implantation (DHI):
A variation of the FUE technique, DHI uses a specialized tool called the Choi implanter pen to directly implant the extracted hair follicles into the recipient area. This method allows for precise control over the angle, depth, and direction of the hair, ensuring an aesthetic and natural outcome.
Your Journey to Fuller Hair Begins Here
Understanding the causes of temple hair loss is crucial, but knowing your options is what truly empowers you. At Musk Clinic, we believe in a holistic, personalized approach. Our team of experienced dermatologists and trichologists will conduct a thorough examination of your scalp and hair and may recommend blood tests to determine the exact cause of your hair loss.
We then create a customized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs, combining the most effective therapies to help you achieve your hair restoration goals. Remember, early intervention is key to achieving the best possible results.
Don't let temple hair loss hold you back any longer. Take the first step towards renewed confidence and a fuller head of hair.
Conclusion
Female temple hair loss, while challenging, is a manageable condition with the right knowledge and professional support. From understanding the root causes to exploring advanced treatment options, you now have a comprehensive guide to help you on your journey.
At Musk Clinic, we are committed to providing expert care in a compassionate and supportive environment. Our goal is not just to treat your hair loss but to restore your self-esteem.
FAQs

Dr. Anand B. Shah
- 10 Years of Experience
Dr Anand B. Shah, is a board-certified Maxillofacial & Craniofacial surgeon who is highly skilled in cosmetic facial and hair restoration surgery and has exclusively practised the same, internationally and nationally.